#being quirky and different by using the titan side of the family instead of the god side lol
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
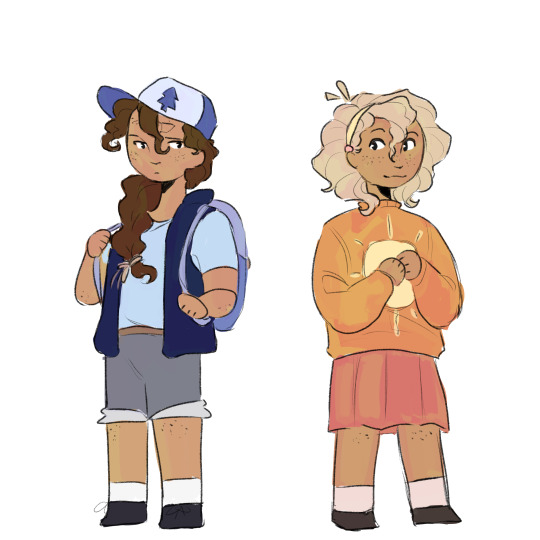
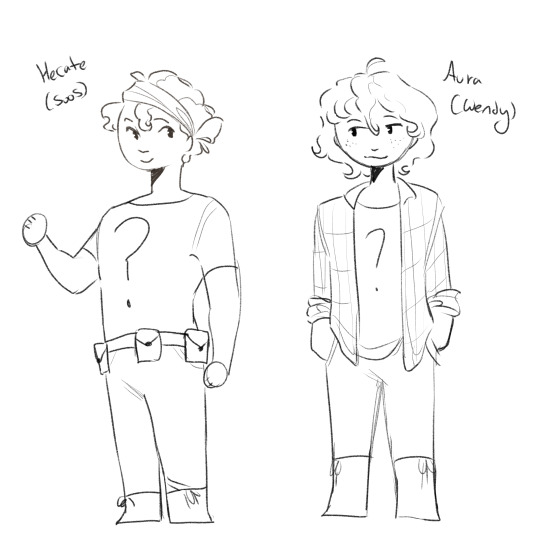






Hey guys crazy idea but like Artemis and Apollo are Dipper and Mabel right? Right? Yeah I got carried away big time but like I think Gravity Falls + Greek Mythology is a banger idea so it's fine.
#trials of apollo#greek mythology#toa apollo#lester papadopoulos#pjo artemis#helios#selene#hecate#aura#khaos#being quirky and different by using the titan side of the family instead of the god side lol#also obvs some dynamics would change#like Artemis wouldn't have a crush on Aura bc they are literally cousins#quickfire of other characters: Gideon = Zephyrus#Pacifica = Nike#Fiddleford = Hypnos#Candy and Grenda = Chiron and Calliope#haha I love Gravity Falls#au#sunny speaks
488 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve been watching so many cartoons for free, good ones and bad ones, that here’s a status update on the ones I know some of you (frequently for the right reasons) wouldn’t even watch if they paid you: Family Guy: now owned by Disney, and it’s obvious they were given strict new rules about what they could and couldn’t joke about, Quagmire isn’t even a sex weirdo anymore and some episodes border on somehow kid-friendly with a smattering of kinda funny inoffensive jokes, but it’s still overall poor quality and the best thing you can say is that it stopped being as cruel to Meg. Some episodes are probably the worst ideas they’ve ever had and for “some reason” the Disney buyout did not change the frequency or nature of its scattered Jewish jokes.
South Park: many episodes are the terrible takes and bland running gags you remember, and even when they aren’t that bad on paper, the jokes just don’t land for me. Oftentimes the whole joke is that someone, usually Randy, is dramatically overreacting to something trivial. I will say that after they were criticized for preaching apathetic, lazy centrism to their fans, they’ve increasingly taken blunt sides in controversial topics and almost gone overboard to leave no ambiguity. I had to cut out a detailed example here because a few people skimmed it and thought I was literally saying South Park is good now, which it isn’t.
Rick and Morty: I haven’t watched the new one but I know a lot of people stopped years ago or never even started, though it can have earnestly creative science fiction scenarios and a lot of funny bits that are unfortunately never the ones that go viral. Almost any joke that isn’t tryhard mean tends to be at least okay. For the last season or so, Rick has still been a generally unfunny asshole, but he has generated more entertainment by suffering more satisfying consequences and humiliation for his selfish personality. Morty by this point is even written completely aware that his grandpa sucks and uses everybody and gets the last laugh over Rick in a lot of stories. Overall it’s still trying to be edgier and more cynical than I think anyone really likes these days, and just has really stark ups and downs.
Teen Titans Go: this isn’t one of the shows people blast as cruel or offensive or anything but a lot of people older than its main viewership really really resent it. This is a shame because some of it is still funny regardless of your age or your ambivalence to superheroes (me) while sometimes they just do cute quirky things with their access to WB properties. One episode has them fighting Beetlejuice (though the gags are all lifted 1:1 from the original movie, which is kind of hit or miss) and more recently they did a crossover with Freakazoid. They also have this strange, more serious (but still deeply absurd) sci-fi AU setting with big budget art direction, which did so well in ratings that it’s getting its own spinoff.
American Dad: I made some posts about this ages ago but this series was bought by a different network, got different writers and drifted so far from its original “political family guy” angle that many episodes don’t even have edgy or nasty humor and are instead just obtuse, niche nonsense, as if the writers want to see how many viewers they can alienate. If you’re both bored and curious you can just read the episode summaries on wikipedia from about season 14 and up until you hit one that sounds like an algorithmic shitpost, like that one I think I showed a clip from once in which Santa Claus is excavating the corpse of the giant Humbaba from the Epic of Gilgamesh so he can receive Humbaba’s Seven Radiances. He believes this is how he can finally end his curse, which we call Christmas, and will then be free to do what he really wants, which is kill people.
I edited a bunch of this for clarity but I still don’t know how anybody thought I was actively promoting things like South Park, I think I’m pretty clear here that I just watch a mix of things I like and dislike?
603 notes
·
View notes
Text
Treat Your S(h)elf: Imperial Boredom: Monotony and the British Empire by Jeffrey A. Auerbach (2018)

The British Empire has had a huge impact on the world in which we live. A brief look at an atlas from before World War One will show over hundred colonies that were then part of the Empire but now are part of or wholly sovereign states. Within these states much remains of the commercial, industrial, legal, political and cultural apparatus set up by the British. In many former colonial areas, political issues remain to be solved that had their genesis during the British era.
The legacy of the British has been varied and complex but in recent years much attention has been on making value judgements about whether the Empire was a good or bad thing. Of course the British Empire was built on the use of and the continual threat of state violence and there were appalling examples of the use of force. As well as the slave trade, there was the Amritsar Massacre in 1919, the 1831 Jamaican Christmas Uprising, the Boer War concentration camps (1899-1902) and the bloody response to the Indian Mutiny of 1857. However, we must not just focus on these events but examine the Empire in all of its complexities.
In the current moment of our times, it would seem that as a nation we are more concerned about beating ourselves up and making the nation feel guilty than understanding how and why the British came to exist, and setting the growth of the British Empire into historical context to be wise about the good, the bad, and the ugly. History has to be scrupulously honest if it’s not to fall prey to propaganda on either side of the extreme political spectrum.
Truth be told I find these questions about the British Empire being good or bad either boring or unhelpful. It doesn’t really bring us closer to the complexity and the reality of what the British Empire was and how it was really run and experienced by everyone.

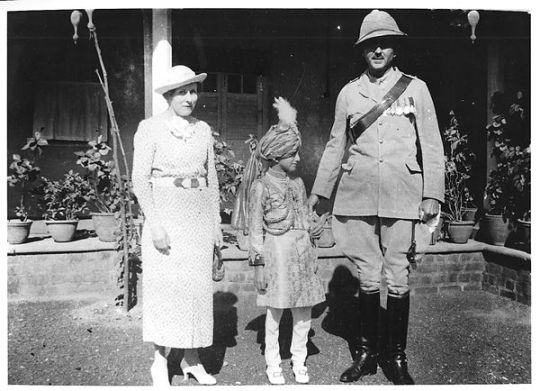
For myself personally the British Empire was part of the fabric of our family history. The Far East, the Middle East and Africa figured prominently and at the centre of which - the jewel in the crown so to speak - was India. In my wider family clan I’ve come to learn about - through handed down family tales, personal diaries, private papers, and photos etc - the diverse experiences of what certain eccentric characters got up to and they ranged from missionaries in India and Africa to military men strewn across the Empire, from titans of commerce in the Far East to tea farmers in East Africa, from senior colonial civil servants in Delhi to soldier-spies on the North West Frontier (now northern Pakistan).
My own experience of being raised in India, Pakistan as well as parts of the Far East was an adventure before being carted off to boarding school back in Britain and then fortunate in later life to be able to travel forth to these memorable childhood places because of the nature of my work. Having learned the local languages and respectful of customs I have always loved to travel and explore deeper into these profound non-Western cultures. Despite the shadow of the empire of the past I am always received with such down to earth kindness and we share a good laugh. So I always assumed that the British Empire played a central role in the life of Britain has it had in our family history just because it was there. But historians are more concerned with much more interesting questions that challenge our assumptions.


So when I was at university it was a great surprise to me to first read a fascinating history of the British Empire by Bernard Porter called ‘The Absent Minded Imperialists: Empire, Society and Culture in Britain’ (2004). Porter was, in his own words, “mainly a response to certain scholars (and some others) who, I felt, had hitherto simplified and exaggerated the impact of ‘imperialism’ on Britain in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, after years in which, except by empire specialists like myself, it had been rather ignored and underplayed. […] the main argument of the book was this: that the ordinary Briton’s relationship to the Empire in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries was complex and ambivalent, less soaked in or affected by imperialism than these other scholars claimed – to the extent that many English people, at any rate, possibly even a majority, were almost entirely ignorant of it for most of the nineteenth century.” It became a controversial book but a welcome one because it was well researched and no doubt made some imperial historians choke on their tea dipped biscuits (and that’s not even counting the historically illiterate post-colonial studies crowd in their English faculties who often got their knickers in a twist).
Years later I read another fascinating collection of scholarly chapters by different historians called ‘Anxieties, Fears, and Panic in Colonial Settings: Empires on the Verge of a Nervous Breakdown’ (2016) edited Harald Fischer-Tiné which challenged a rosy vision of Britain’s imperial past by tracing British imperial emotions: the feelings of fear, anxiety, and panic that gripped many Britons as they moved to foreign lands. To be fair both Robert Peckham’s Empires of Panic: Epidemics and Colonial Anxieties (2015) got there before him but Tiné’s history set the trend for others to follow such as Marc Condos’s The Insecurity State: Punjab and the Making of Colonial Power in British India (2018) and Kim Wagner’s Amritsar 1919: An Empire of Fear and the Making of a Massacre (2019).
They all set out their stall by highlighting the sense of vulnerability felt by the British in the colonies. Fisher-Tiné’s edited book in particular highlights the pervasiveness of feelings of fear, anxiety, and panic in many colonial sites. He acknowledges that: “the history of colonial empires has been shaped to a considerable extent by negative emotions such as anxiety, fear and embarrassment, as well as by the regular occurrence of panics.”
The book suggests that these excessive emotional states were triggered by three main causes. First, the European population in British India was heavily dependent on Indian servants and subordinates who might retaliate against unfair masters or whose access to European dwellings could be used by malevolent others to poison the white elite. Second, anxieties about the assumed toxic effects of the Indian climate fuelled also poisoning panics. Diseases such as malaria and cholera were considered to be the ultimate outcome of an “atmospheric poison”. Third, Indian therapeutics and the system of medicine were also identified as a potential cause of poisoning European communities. These poisoning panics only helped reinforce the racial categorisations of Indians, the moral supremacy of the white population, and the legitimacy of colonial rule. Overall the book expanded the understanding of how a sense of fragility rather than strength shaped colonial policies.

Now comes another noteworthy book which again sound a little quirky but is no less meticulous in its research and judicious in its observations. Many books about the British Empire focus on what happened; this book concentrates on how people felt. When I was first given it I was predisposed to be negative because here was a book about ‘feelings’ - the current disease of our decaying western culture. But I was pleasantly surprised.
Was the British Empire boring? So asks Jeffrey Auerbach in his irreverent tome, ‘Imperial Boredom: Monotony and the British Empire’ (2018).
It’s an unexpected question, largely because imperial culture was so conspicuously saturated with a sense of adventure. The exploits of explorers, soldiers and proconsuls – dramatised in Boys’ Own-style narratives – captured the imagination of contemporaries and coloured views of Empire for a long time after its end. Even latter-day historians committed to Marxist or postcolonial critiques of Empire tend to assume that the imperialists themselves mostly had a good time. Along with material opportunities for upward mobility, Empire offered what the Pan-Africanist W.E.B. DuBois called ‘the wages of whiteness’ – the psychological satisfactions of membership in a privileged caste – and an escape from the tedium of everyday life in a crowded, urbanised, ever less picturesque Britain.
The British Empire has been firmly tied to myth, adventure, and victory. For many Britons, “the empire was the mythic landscape of romance and adventure. It was that quarter of the globe that was coloured and included darkest Africa and the mysterious East.” Cultural artifacts such as music, films, cigarette cards, and fiction have long constructed and reflected this rosy vision of the empire as a place of adventure and excitement.
Against this widely held view of the empire, As Auerbach argues here, however, the idea of Empire-as-adventure-story is a misleading one. For contemporaries, the promise of exotic thrills in distant lands built up expectations which inevitably collided with reality.
In a well-researched and enjoyable book, the author argues “that despite the many and famous tales of glory and adventure, a significant and overlooked feature of the nineteenth-century British imperial experience was boredom and disappointment.” In other words, instead of focusing on the exploits of imperial luminaries such as Walter Raleigh, James Cook, Robert Clive, David Livingstone, Cecil Rhodes and others, Auerbach says pay attention to the moments when many travellers, colonial officers, governors, soldiers, and settlers who were gripped by an intense sense of boredom in India, Australia, and southern Africa.
For historians, the challenge is to look past the artifice of texts which conceal and compensate for long stretches of boredom to unravel the truth. Turning away from published memoirs and famous images, therefore, Auerbach trains his eye on the rough drafts of imperial culture: letters, diaries, drawings. He finds that Britons’ quests for novelty, variety and sensory delight in the embrace of 19th-century Empire very often ended in tears. Indeed Auerbach identifies an overwhelming emotion that filled the psyche of many Britons as they moved to new lands: imperial boredom.

Precision in language and terminology is essential and Auerbach begins by setting out what he means by boredom. Adopting Patricia Meyer Spacks’ approach, he points out that the term first came into use in the mid-18th century. Auerbach identifies then the feeling as a “modern construct” closely associated with the mid-18th century where the spread of industrial capitalism and the Enlightenment emphasis on individual rights and happiness that the concept came to the fore. This does not mean that nobody previously suffered from boredom, but that, with the Enlightenment’s emphasis on the individual, this was when the feeling first became conceptualised. Like Spacks, he distinguishes boredom from 19th-century ‘ennui’ or existential world-weariness and also from monotony, which has a much longer history. Whilst a monotonous activity or experience may generate a feeling of boredom, it will not necessarily do so. The two terms must, therefore, not be equated.
Significantly, in a footnote, Auerbach cites a passage from 19th Century English satirical novelist, Fanny Burney, in which an individual is described as ‘monotonous and tiresome’ but, as he emphasises, ‘not boring’. To prevent confusion, the term ‘boring’ is best avoided when describing an activity or experience because this is to beg the question as to whether it does in fact generate feelings of boredom in a particular person.

How then should this state of mind be assessed and what should be seen as the symptoms of imperial boredom? As Auerbach acknowledges, boredom ‘is not a simple emotion, but rather a complex constellation of reactions’. Building on that approach, he says ‘imperial boredom’ reflected ‘a sense of dissatisfaction and disenchantment with the immediate and the particular, and at times with the enterprise of empire more broadly’. If this tends to mix cause and effect, the idea of dissatisfaction and disenchantment essentially mirrors Spacks’ definition of the symptoms of boredom, namely, ‘the incapacity to engage fully: with people, with action, with one’s own ideas’. ‘Imperial boredom’, therefore, was more than a fleeting moment of irritation with a particular situation or person and reflected a mind-set that derived from, and in turn, further contributed to, a sense of disillusionment with the overall project.
It stemmed, so Auerbach argues, from the marked contrast between how empire was represented and how it turned out to be, between ‘the fantasy and the reality’. ‘Empire was constructed as a place of adventure, excitement and picturesque beauty’ but too often lacked these features. Nowhere is this better described than in George Orwell’s Burmese Days, in which the promising young John Flory has become ‘yellow, thin, drunken almost middle-aged’. Beginning with this illustration, Auerbach argues that historians have too often overlooked this essential aspect of empire and sets out to discover the extent to which it was characteristic of what Flory called the ‘Pox Britannica’ more generally.

During the 17th century the British Empire sustained itself on the story that the colonial experience was both righteous and unbelievably exciting. Sea voyages were difficult, and when one eventually did reach landfall there was a good chance of violence, but the exotic foreign cultures, the landscapes, and the wildlife made the trip worthwhile. The British colonialist was meant to be swashbuckling. Advertisements for even the most banal household goods offered colourful and robust propaganda for life in the colonies. Travelogues and illustrated accounts of colonial exploration were wildly lucrative for London publishing houses. All of this attracted a crowd of young Brits eager to escape the drudgery of life in the metropole.
By the 19th century, expectations were catching up. As Auerbach makes it clear, from the beginning, the sense of boredom experienced by many Britons in new colonial settings was much more profound during the nineteenth century. Indeed, the latter was marked by a series of bewildering social, cultural, and technological changes that stripped the empire of its sense of novelty. The development of new means of transport such as steamships, the rise of tourism, and the proliferation of guidebooks jeopardised the sense of risk, newness, enthusiasm that had long been associated with the British imperial experience. Consequently, while “the early empire may have been about wonder and marvel, the nineteenth century was far less exciting and satisfying project.

Auerbach spent 20 years gathering evidence spanning the late 18th century to the turn of the 20th, which records feelings of being bored, miserable and deflated. It’s a captivating history of imperial tedium drawn from memoirs, diaries, private letters and official correspondence. In “reading against the grain”, as Auerbach puts it, he has focused on recorded events normally skimmed over by historians, precisely for being boring – multiple entries repeated over and over again about the weather, train times, shipping forecasts, deliveries, lists and marching; or about nothing ever happening.
In five thematic chapters, “Voyages”, Landscapes,” Governors,” Soldiers”, and “Settlers,” Auerbach shines new light on the experience of traversing, viewing, governing, defending and settling the empire from the mid-eighteenth century to the early twentieth century. The monotonous nature of the sea voyage, dreary and uninteresting imperial lands, daily routine, depressingly dull dispatches, mind-numbing meetings are some of the sources of an utter sense of imperial boredom.

Whilst the first chapter, Voyages, may be the logical starting-point, it presents particular problems. They may have been monotonous, but it is unlikely that they would have engendered feelings of disenchantment and disillusion at the outset of an empire life or career. Auerbach begins with the somewhat surprising assertion that ‘not until the first half of the 19th century did long-distance ocean travel become truly monotonous’, arguing that this was because, until then, the weather had been ‘a source of danger and discomfort’ whereas, by the mid-19th century, ‘it was barely worth mentioning’. Leaving aside the obvious difficulties with that approach – many 19th-century travellers, assuming they survived, described enduring terrifying typhoons in the Indian Ocean and South China Sea – voyages certainly could be monotonous, particularly, when steam replaced sail.
However, his assertion that this ‘helped to produce feelings of boredom that had never been felt before’ is more questionable. For example, whilst Sir Edmund Fremantle (1836–1929) wrote in his memoirs that, although the sea passages were ‘monotonous’, ‘it never occurred to [him] to be bored’, Auerbach suggests that, ‘in several places his memories [sic] belie his claims’, in that they refer to the ‘the monotony’ of various experiences, including cruising out of harbour under steam rather than under sail, which ‘always possessed some interest’. But, this not only contradicts what Fremantle wrote but also equates boredom with monotony and, thus, deprives it of any proper meaning.

Similarly, because the Royal Naval Surgeon, Edward Cree (1814–1901) recorded his passing the time ‘reading, drawing, walking on deck, eating drinking and sleeping’, Auerbach concludes that ‘almost every leg of his 1839 journey to the East was boring or disappointing’. However, he omits the opening words of this journal entry which reads, ‘making but slow progress towards China. Weather intolerably hot … The time passes pleasantly enough on board’, which suggests he was certainly not bored. Much of this chapter is not concerned with monotony but with how ‘dreadful’ sea voyages could be, particularly, for travellers to Australia, most of all transported convicts, who, as he shows, had to endure the most brutal conditions. But they had no expectations of empire and this seems to add little to the understanding of imperial boredom.
It may well be that, because voyages were so unpleasant, travellers became all the more expectant and thus disappointed, when, on arriving, they found, as Auerbach argues in the next chapter, that much of the landscape was dreary and uninteresting. Moreover, many could not decide whether they were in search of a landscape that was picturesque and exotic or ‘normalised’ by reproducing English architecture, gardens and surroundings. This dichotomy generated further disenchantment.
If Auerbach dwells too long on obscure painters who often had little success in making these imperial landscapes picturesque, there is no doubt that many of them were monotonous, not least the vast tracts of Australian out- back. Consequently, whilst ‘the early empire may have been about wonder and marvel, the 19th century was a far less exciting and satisfying project’ and this contributed to feelings of boredom.

In the chapter, ‘Governors’, Auerbach essentially covers the administration of the empire. Here, there was also a lot of monotony, although Auerbach wavers between whether this was caused by having too much or too little work to do. Either way, it leads to the assertion that ‘throughout the nineteenth century and into the twentieth, British imperial administrators at all levels were bored by their experience, serving king or queen and country’. However, this is qualified in the next paragraph, in which he cites the Marquess of Hastings, who served in India in the early 1800s, and Lord Curzon, who served as Viceroy at the end of the century, neither of whom, he says, suffered from boredom. It was ‘during the middle decades, that imperial service was far less stimulating’ but he does not explain why it should have been limited to this particular phase.
Indeed, in terms of the staggering quantity of paper generated by the ICS, the problem stretched back to the early 18th century. Records were copied and recopied, and months were spent waiting on instruction from London. The few encounters with colonised subjects came in the form of long, drawn-out formal events. Lord Lytton as Viceroy of India between 1876-1880 was required to bow 1230 times during one particularly ceremonial reception with the Viceroy.
Whilst it is ultimately fruitless to exchange examples of officials who did and did not find government service boring, some of those chosen by Auerbach are not convincing. James Pope Hennessy, for example, the eccentric Irishman who delighted in antagonising the colonials and endearing himself to the indigenous people with his unconventional views on racial equality, certainly found the European life-style monotonous but, as a result, made sure he kept ceaselessly active. In the words of his biographer, ‘the chief impression [he] made on British and Orientals alike was one of superlative vitality. “He would do better”, wrote Sir Harry Parkes “if he had less life”’, Coming from Parkes, that arch- imperialist, who allegedly died from over-work and could never have been bored, the comment is telling.

While idleness certainly contributed to boredom, it was often the labour of maintaining colonial control that proved to be the most dull. Increasingly professionalised, the management of the colonies became characterised by strict report-making, bookkeeping and low-stakes decision-making related to staff. Whilst these officials may have become disenchanted, it is unclear what sort of mind-set they had when they started out: according to Auerbach, ‘they may well have entered imperial service out of a sense of duty, or perhaps looking forward to a colonial sinecure that offered status and adventure as well as a generous salary, but instead found themselves inundated by a volume of paperwork and official obligations that they had never anticipated, and which they found to be, quite frankly boring’. As a result, they were ‘eager to escape the tedium of the empire they had built’.
Whilst this suggests that, as a result, they threw up their empire careers, the example of Sir Frank Swettenham does not seem to fit the picture. He may have found life from time to time ‘extraordinarily dull’, but he continued as a government official in the Malay States for thirty years, before retiring in 1901. His belief in the imperial cause seems to have overcome the dullness and trumped any possible disenchantment.
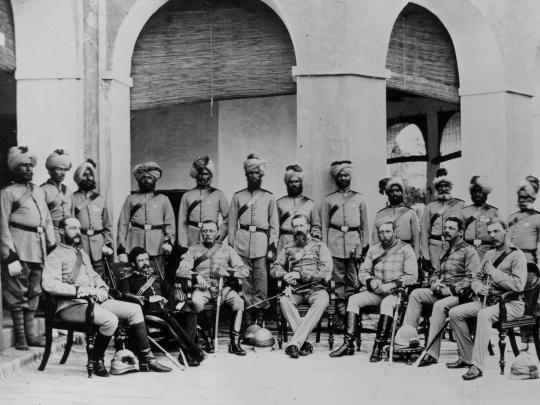

In the chapter entitled, Soldiers, Auerbach concedes that ‘the link between military service and boredom can be traced at least to the mid-eighteenth century’. However, he argues, what was different in the 19th century was that boredom was no longer simply ‘incidental or ‘peripheral;’ it was ‘omnipresent’ and this was ‘a function of unmet expectations’, namely, the unsatisfied thirst for action and bloody combat as the ‘small wars’ of the Victorian age became shorter and fewer. However, citing Maeland and Brunstad’s Enduring Military Boredom, he concedes that this omnipresent boredom is a ‘condition that persists to the present day, especially among enlisted men’. This, therefore, divests it of any imperial character and suggests that it was, and remains a feature of modern military service.
Nonetheless, it would have been interesting to know how this boredom affected the performance of the military in the context of empire. Certainly, it gave rise to some of its more unsavoury aspects, with drunken soldiers brawling and beating up the locals and spending much of their time in the local brothels.
According to Richard Holmes, by 1899, there was ‘a real crisis’ in the infection rates of venereal disease of British soldiers in the Indian Army: ‘for every genteel bungalow on the cantonment … there were a dozen young men, denizens of a wholly different world, crossing the cultural divide every night’. Here was imperial boredom in the raw and urgent measures had to be taken to abate its consequences.

Although the final chapter is entitled ‘Settlers’, it encompasses a much broader category of imperial agents, including women, who until this point have been little- mentioned, and, in particular, women in India ‘most of whom went there in their early twenties to work (or to accompany their husbands who were working) and then typically left by the time they reached their fifties to retire in Britain’. It is unclear why these women and, indeed the whole topic of women in empire, should be subsumed under this chapter heading, given their importance in the empire project and the attention given to them in post-colonial scholarship.
In recent scholarship, empire white women have been frequently misrepresented and lampooned in the literature, including the novels of E. M. Forster, George Orwell, and Paul Scott and all too often reincarnated as representing the worst side of the ruling group – its racism, petty snobbishness and pervading aura of superiority and shown as shallow, self-centred and pre-occupied with maintaining the hierarchy of their narrow social worlds. They have invariably been portrayed as both bored and boring.
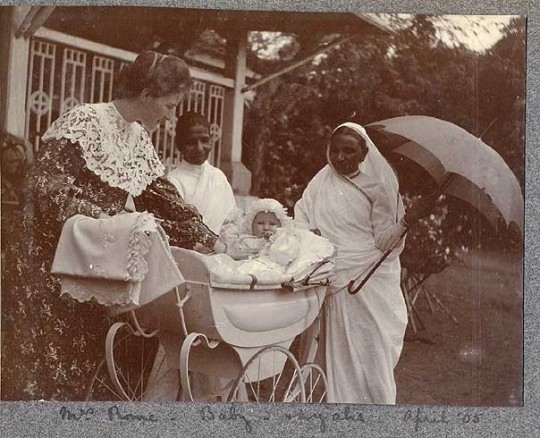

The wives of these officials were encouraged to run their households in a similar way, managing a large domestic staff and keeping a meticulous watch on financial expenditures. Socially, they were faced with constant garden parties and dinners with whatever small group of colonial families lived nearby. It’s difficult to imagine just how dull the existence of these administrators must have been, yet in reading these colonial accounts, the temporality and the totalising effects of boredom feel undeniably similar to the way that we describe the monotony of work today.
Auerbach effectively reiterates the trope as a clichéd illustration of a female, reclining aimlessly on a chaise longue, conjuring up the familiar image of ‘the same women [who] met day after day to eat the same meals and exchange the same banal pleasantries’ and concluding that ‘it was not only in India that women were bored, which suggests that the phenomenon was not a localised one, but a broader imperial one’.
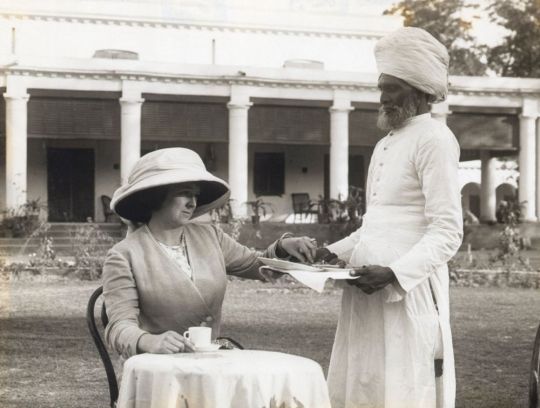

Of course many western women did find life in empire monotonous and suffered from boredom, if not depression, and no doubt many were insufferable, as were their husbands, but there is an alternative image and the analysis is so generalised that their contribution is, once again, in danger of being dismissed out of hand.
A more nuanced approach would have examined ways in which women overcame their boredom by pursuing activities in which they were anything but bored, including, most obviously, the missions, a category which, despite its importance, does not feature, save for one cursory comment to the effect that, ‘even missionary women, whose sense of purpose presumably kept them inspired, could find themselves bored’. The example given is that of Elizabeth Lees Price, who, at one point during her eventful life, had to help run three schools for 30,000 pupils. But, just because her diary recorded ‘with increasing frequency’ the comment ‘nothing has happened’, it seems a stretch to infer, as Auerbach does, that ‘not even missionary work was enough to stave off the boredom that afflicted women all across the empire’.
For Auerbach, recuperating boredom means reframing the experience of empire as one of failure and disappointment. In the context of colonial scholarship, which tends to focus on the violence of colonialism and the myth-making that went along with it, Auerbach’s book is rather counter-intuitive. He drains the power of these myths, looking instead at the accounts of those responsible for building empire from the ground up: “What if they were not heroes or villains, builders or destroyers,” he writes, “but merely unexceptional men and women, young and old, rich and poor, struggling, often without success, to find happiness and economic security in an increasingly alienating world?” The agents of colonialism struggled to find any semblance of agency in the work that they were doing. Imperial time stretched out, deadened over decades of appointment in far off islands and desert outposts: a sort of watered down version of Hannah Arendt’s “banality of evil” in paradise.

Whilst Auerbach demonstrates that much of empire life was monotonous, to my mind, he is too quick to infer that this monotony necessarily gave rise to feelings of ‘imperial boredom’, properly so-called. He also too easily assumes that, where people were bored, this could only operate in a negative way and, whilst he may be right in concluding that, ultimately, ‘the British were, quite simply bored by their empire’, he fails to draw the evidence together to explore what impact imperial boredom had on the development of empire, for better or worse, during the long 19th century.
If not quite an invention of the 19th century, boredom was a particular preoccupation of the period: the product of new assumptions about the separation of work and leisure and a prominent theme of fin-de-siècle literature. Less clear is whether Auerbach is right to treat boredom separately from other emotional states – anxiety, loneliness, anger, fear – which afflicted the imperialist psyche. After all, a long literary tradition – from Conrad to Maugham, Orwell, Lessing and Greene – describes precisely how those varied shades of neurosis blended into one another.

Besides, a more capacious history of discontent and Empire might help to connect the frustrations of the imperialist experience to the suffering of imperial subjects. When, for instance, did boredom turn to aggression and violence? One danger of Auerbach’s approach in Imperial Boredom is to portray an enervated and under-stimulated, yet still extraordinarily powerful, elite as more or less passive.
As imperial rivalry intensified towards the end of the century, so did the quest for new ways of staving off boredom, not only for men in the British Empire but also for those in the other European empires, and war was one of the most obvious solutions.
As other imperial historians have argued, what Europeans were seeking was everything the nineteenth century, in its drawn-out tedium, had denied them. War as Cambridge historian Christopher Clark has argued, “was going to empower them and restore a sense of agency to their limbs and lives.” Auerbach refers to what Clark called ‘the pleasure culture of war’, citing the example of Adrian de Wiart who, serving in the Boer War, knew ‘once and for all, that war was in my blood. I was determined to fight and I didn’t mind who or what’. But he does not explore the consequences of this mood further, other than to say that these adventurers also ‘ended up bored … and disillusioned’. But, the implications were, arguably, much more far-reaching.
Even if it was not directly causative, this mood was ‘permissive’ of the more direct causes and certainly formed part of the background against which Europe went to war in 1914. It may be thought that it did so in a fit of imperial boredom.

I admire the audacity of Auerbach’s writing and as a revisionist piece of history it has the dash and dare of British imperialism and colonialism. But after reading the book I came away thinking that sweeping statements such as that the empire developed “in a fit of boredom” are a tad unconvincing.
Although he spent about 20 years collecting materials, Auerbach seems not to have visited Africa or India during his research. Had he done so, I doubt if he would all too easily accepted that colonial accounts of being bored represented the full experience. Absent are deeper discussions of how expressions of being bored are linked to racism, arrogance and the need to assert power in exotic, challenging and unstable environments. Emotional detachment, disdain and a demand to be entertained were also part of a well-rehearsed repertoire of domination.
But where Auerbach does succeed is in admirably capturing the texture of everyday imperialist life as few historians have. Most of these examples are compellingly relevant and illustrative of some of the colonial circumstances that drove Britons mad with boredom, challenging one of the enduring myths about the British Empire as a site of exciting adventure.

If you are a lover of histories of white imperial rulers and thumbnail portraits, this book is for you. It’s full of excellent quotes. Lord Lytton, for example, fourth choice to be governor-general of India in 1875 (and appalled by the prospect), later summed up the British Raj as “a despotism of office-boxes tempered by the occasional loss of keys”. It was certainly the case that propaganda about empire and the populist books written about it to make money created false expectations, leading to bitter disillusionment. Nostalgists for the age of pith helmets and pukka sahibs will find little comfort here.
In mining the gap between public bombast and private disillusionment, Auerbach demonstrates that – even for its most privileged beneficiaries – Empire was almost never a place where fantasy became reality. I would suggest that rather than the British Empire being mostly boring, more accurate would be David Livingstone’s verdict on exploratory travel while battling dysentery: “it’s not all fun you know.”
The concept of imperial boredom provides a novel and illuminating lens through which to examine the mind-set of men and women working and living in empire, how it was that, despite the crushing monotony, so many persisted in the endeavour and what this tells us about the empire project more generally. There are all states of mind familiar to historians of empire (in the lives of their subjects, of course). It has long been argued that strategies to relieve moments of white boredom in the empire included cheating and adultery, husband hunting, trophy wife hunting, massive consumption of alcohol, gambling, copious diary and letter writing, taxidermy, berating the servants, prostitution, bird-watching, game hunting, high tea on the verandah, fine pearls and ball gowns, all were par for course in the every day lives for those bored British colonisers.
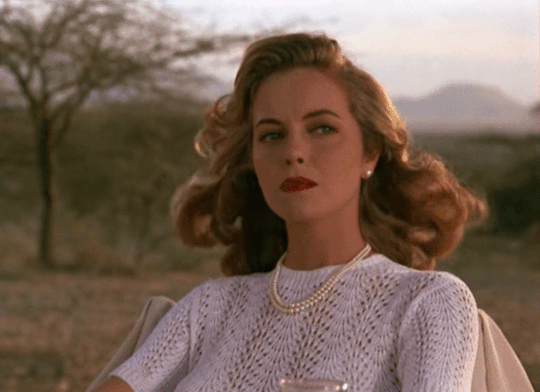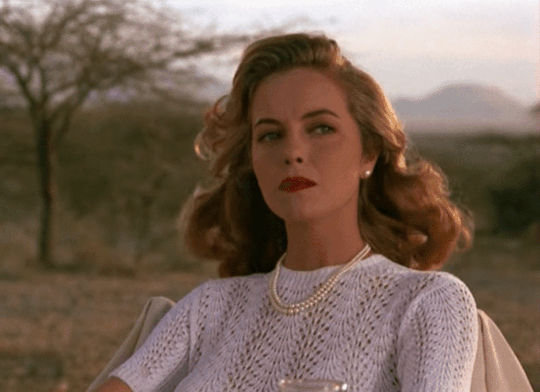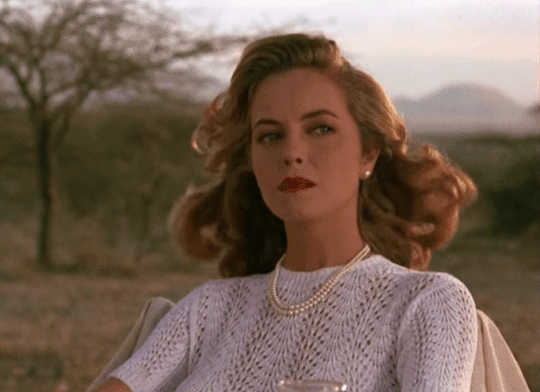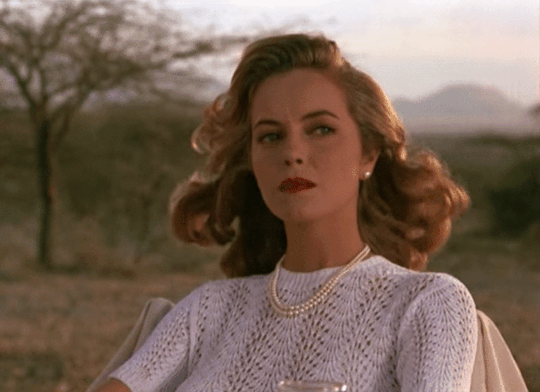
Auerbach’s book reminds me of a not so nice female character bemoans James Fox’s scandalous but true to life colonial novel White Mischief (1982), as she looked out over the Rift Valley in 1940s colonial Kenya, she declares, “Oh God! Not another fucking beautiful day.”
An earnest post-colonialist studies reader might might feel triggered by such a flippant remark as evidence of all that was wrong with the imperial project but at heart it’s a pitiful lament disguised as boredom at the gilded cage the British built for themselves to capture the enchantment and disenchantment of every day life in the British Empire.
#treat your s(h)elf#books#book review#bookgasm#reading#imperialism#british empire#boredom#british#history#colonialism#imperial boredom#jeffrey auerbach#empire#personal#bio#childhood
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
what does this have to do with clownfish?
i know this was a mostly sad episode that ended on a rather disquieting note, but i was grinning from ear to ear by the end, you guys. I LOVE THIS SILLY SHOW SO MUCH, and i want to tell you why, so let’s talk about titans 2.04:
SPOILERS ahead
1. i get why we’re getting a flashback episode now--the titans’ ~sordid past~ with deathstroke has gotten a fair bit of build-up, and now that slade has jason, we need the history between him and the og team to contextualise the upcoming confrontation. still, i was really looking forward to having kory reunite with the team, goddamit!
1.5. i like the convivial, almost collegiate vibe that the original titans have about them--the idea of them getting together both desperate to prove that they are more than what their origins and youth might suggest, and to dick around (pun not intended) and just... be, in a way that their individual circumstances wouldn’t allow them. costumes on, in mission-mode, they are trained and hyper-competent, but in their downtime they apparently like adorably warbling off-key at each other and re-enacting 90s/00s cheesy rom-coms. it’s great! i would’ve loved to see these kinds of flashbacks drip-fed to us right from the beginning of the season--putting it all in one episode, from aqualad’s introduction to demise all in forty minutes, not only screws up the pacing, but also robs us of more of garth’s genuinely warm chemistry with the rest of the team.
1.67. besides, the immediate contrast between this and the way dick conducts the titans now would’ve been funny and quite impactful.
2. for all that dick seemed standoffish and genuinely frightened of himself in s1, the slightly less filtered look we get into his mind in this flashback--well before his existential crisis--is somehow even more disquieting?? the way he talks about batman and his relationship with dawn and even his friendship with donna smacks of an alarming emotional disconnect; a space where his sense of self has fallen and been replaced by a role that he has been trained to play. he smiles more in this episode than probably all eleven of s1 combined, but he’s far more reserved, afraid of vulnerability, and completely unwilling to express any emotion that would come in the way of him being who he Needs To Be.
2.45. this episode puts into sharp relief just how far dick has come to make peace with bruce in 2.01. here batman is a glowing symbol against the night sky; a shadowy figure promising justice is vengeance and not the other way around; a hulking figure that he can hate and love without reserve, that orders him to be better no matter how exhausted he is, even while standing between him and incomprehensible evil like a bulwark. at the heart of the titans tower--a skyscraper on the opposite side of the country from gotham--is another batcave, a sign that how no matter how far he goes, dick’s perception of himself and his relationships is still inextricably tied to batman and his ways.
it’s the missing link between the angry, grieving boy we saw in flashbacks last season, and the man rapidly spiralling into crisis at the beginning of season 1. he’s internalised batman’s mission before he can decide for himself what he wants to be, and he’s been like this well into his adult years (unlike the comics). no wonder when the moment he goes Too Far finally comes, when he’s so burrowed into himself that vengeance becomes an end rather than a tool, it’s such a violent upheaval, and one that he hasn’t quite been able to put to rest in over a season.
2.65. honestly the matter of fact way he talks about being dawn’s rebound relationship after her breakup is haunting me?? dick grayson--robin, batman’s partner, the First Sidekick, leader of the titans, friend, brother, lover, a valuable asset with trackers in his arm and neck--is so utterly subsumed that his feelings, his self, automatically comes second to the role he’s playing. i wonder if he had found that he’d had a tracker installed in his body without his knowledge at this point, he’d have accepted the cold logic of it (of course batman needs to keep track of him), instead of the visceral reaction he has five years later, when he immediately picks up a knife and cuts it out of his skin.
2.95. (retrospectively it lends so much more meaning to the opening scene of 1.08??? where dick says he needs to go off on his own to get his bearings right instead of staying on to be the Leader after their traumatic time at the asylum and kory and the others are quietly accepting of it?? where’s that ‘that’s growth’ gif when you need it)
3. donna! it’s interesting that her role as a titan was always meant to be a pitstop before she moved on to Greater Things, and her struggle to reconcile that with her growing attachment to the team came across really well. jillian’s never really pressuring her to leave immediately--six months! two weeks! idk, forever! really, it’s your pick!--but donna tells dick she needs to leave that very night, either because she’s hoping that he’ll protest and ask her to stay, or that she’ll fall for garth and lose her wavering conviction to leave if she stayed any longer, or both.
3.5. donna and garth’s relationship followed so many wonderfully cheesy conventions, with all of their attendant adorableness and Problems. the scions of two different royal families of two different races falling in Forbidden Love! garth clumsily flirting with donna even as she keeps turning him down! (not cool, garth!) bonding over reminiscing about quirky childhood memories! consulting a put-upon mutual best friend! the last minute reconciliation and confession of love at the airport! garth dying right after celebrating his birthday! (that cop was just a day away from retirement!) PERFECT
like. i have NO IDEA why people still insist on calling this show ‘dark’ and ‘edgy’. don’t let the weird lighting and occasional blood spatter distract you from the goofy, well-intentioned heart right at its centre, you guys!
(but man, dick and donna’s quiet heartbreak at the prospect of separation was harder to watch. for a moment, dick really let himself feel the burden, sinking onto his haunches, his head in his hand like he was about to cry. just a moment.)
4. the others’ reaction to garth’s death is very telling. donna is devastated; hank and dawn are upset, but in a distant way that suggests that they didn’t really know him very well or for very long; and dick... well dick is hard at work in his batcave, because that is how he knows to react to disaster.
4.5. i know that i spend quite a bit of my reviews harping on and on about dick, but he is more than just the team leader, or the one with the most well-defined arc so far, or the connective tissue between the old and new teams: the titans is HIS, in ways both subtle and insubtle. batman is funding the whole thing; their resources, their tech? all wayne enterprises. by extension, this shindig is dick’s idea, dick’s operation, something he shaped after himself--serene, beautiful, somewhat impersonal on the surface and batman-the-symbol, batman-the-phantom, right at the centre.
4.65. so when the burden of morality-bending vengeance falls squarely on dick’s shoulders, it seems natural. it also seems entirely natural that when dick does follow through on what the team wants from him, the fallout is also put square on him: he’s the one that’s gone completely off the rails, the one that would sacrifice anything for a mission (like hank implies in the previous episode), the one haunted by his own darkness. this, of course, is patently false, as trigon demonstrated earlier this season.
5. the opening scene of slade wilson doing the Thing He Does Best was so fun to watch. i love that this show is always trying to do interesting things with the camera. (tho i wonder, who hired him to take out donna troy in san fran? was that even his original objective? was it dr light? i am Confusion)
5.5. ... even tho the villain-confrontation scenes seemed hampered by low effects budgets and a lack of... kineticism. i can’t figure out how dr light works even after two episodes of seeing him do his thing. he can apparently implant light bombs in people but never seems to use this awesome ability again, when it can actually help him against the titans?
6. the moment i saw joey wilson’s profile through the window of his home, i knew he was going to be my favourite character on this show. i love him and his enthusiasm and his cute shoes and his love for vintage records SO MUCH! i know it’s been hinted that he died, but i can’t bear the prospect for even a second. HE’S ALIVE AND WELL SOMEWHERE HAVING TEA AND LISTENING TO GREAT MUSIC WITH AMY ROHRBACH, I JUST KNOW IT
6.5. dick (and the others) wouldn’t be so horrified with themselves and think about shuttering the titans for good if they hadn’t felt some kind of attachment to jericho. dick especially i think is going to fall into an actual honest friendship with joey and is going to extremely disgusted with himself when it all ends in tragedy anyway.
6.75. we’re probably not going to find out what actually happened to joey for a while, but here’s hoping the Unforgivable won’t happen.
7. on the brightside tho, KORY’S BACK NEXT EP! can’t wait.
63 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have any advice for a new blog?
🌸 Oh this is such an interesting ask, I’ve been thinking about it for a few days now, sorry it’s taken a while to get back to you but I was thinking how best to answer it! While this blog has only been around for 3 years and I’ve only really started posting in it recently, I have had my main tumblr blog for 10 years and several side blogs with quite a few followers so I’m hoping I can provide some insight! I do apologise as this turned into a bit of a ramble that I feel is about tumblr but beings to overlap into life advice lol - I blame my age. 🌸
1.) I would say firstly, enjoy it. I feel sometimes there’s a lot of pressure to get loads of followers, create new content etc. and you can forget why you’re here. I got tumblr to reblog photos of things that made me happy from bands to tattoos, movie stuff, art etc and occasionally I would forget that and end up getting bogged down in comparing stats and myself to others. So yeah, enjoy it and remember why you joined ^_^
2.) If you love work that others create (writing/art/gif sets etc.) show your appreciation not just with likes but with comments and reblogging where you can/feel comfortable doing so. Likes are great and always appreciated but comments help to inspire and reblogging means more people will see their work. It encourages content creators to continue creating, it’s also a really good way of gaining followers and make friends. If you support others they will likely support you in return.
3.) Share the art/fan art/cosplay photos you love as per above - but don’t repost work. This was something I wasn’t really aware of when I first joined tumblr, a lot of people would just save photos from google or deviant art (it was a very different place back then) and post them on tumblr to show appreciation. But often there would be no artist detail or link to the artist, instead if you find something you like reblog it from the creator. If it isn’t on tumblr and you’d really like to post it here, contact the creator and ask their permission to post - then include a link in the post and explain you have the artist’s permission.
4.) Talk to people :) - Okay like Alice in Wonderland here’s some advice I could really use sometimes! Through tumblr I have met some of the most amazing friends. When I first started out I started chatting to a girl who went to the same Uni as me, we met up to go for coffee, browse record shops and saw The Vaccines together. I’ve also met numerous people who encouraged me to go to Hobbit Con in Germany - I had the most amazing time, remained friends, one of them came to my wedding. I guess the message here is that internet friends are great and you never know what a friendship can blossom into. If there’s someone whose work you admire or blog you love, don’t be afraid to reach out and send a message, even if you feel a bit silly (I often do!).
5.) Tags - My take on tags is pretty simple, tag correctly. I often tag things quite heavily but I make sure that I only tag characters that feature in a post or fandoms that feature in that post etc. You often come across posts where every character in the show has been tagged, I get why people do it, it means the post will come up in more results but it is rather infuriating when you’re looking for something specific. It also looks messy and can make things hard to find on your own blog. So yeah tag the show/film/book etc, tag the relevant characters, add whatever tags you want regarding your feelings/emotions about the post or thoughts on it. But ideally keep it relevant. On that note, tag ships (people often blacklist ships they dislike or that they find problematic) so doing this helps everyone. Anything that’s only really suitable for people 18+ tag however you see fit (due to Tumblr’s changes last year we had to revert to tagging things on the citrus scale again so I tag anything like that as lemon as well as nsft) Finally Trigger/content warnings - I do use them, some people put warnings on everything, some people don’t do at all. Again like with shipping it is helpful for people who have
6.) Remember to take breaks - tumblr can be a little addictive and easy to pass time (like social media) so remember to take breaks, when you get back they’ll be loads of new stuff on your dashboard to look at ^_^
7.) Follow loads of blogs! I probably should have put this higher up. But have a think about the kind of content you want to see and spend some time searching for blogs that fit that, I also find it’s nice to follow some more aesthetic blogs or blogs that are calming/relaxing, seeing things like that on my dash is always a reminder to have a breather!
8.) Enjoy playing around with themes - decide what you want your blog to be about (and remember there’s nothing wrong with having a main blog that’s a little bit of everything you love as well as personal stuff!) and then have fun with the settings. There’s a lot of free tumblr themes, some of which are pretty neat and user friendly in terms of customisation. Don’t be afraid to ask questions if you’re stuck.
9.) Side blogs are also really great. I begun to create side blogs because I didn’t want to spam my main blog with Game of Thrones, The Hobbit, Red Dead Redemption 2 or Attack on Titan, so I created side blogs. I still post about all these things on main but not as frequently. A side blog can also be good if you want to create a blog you can share with employers - I have a side blog for my photography and one for my writing. Sideblogs are also a good way of keeping certain material away from the blog where people in real life are most likely to find you. Generally I won’t post 18+ material on my main blog, so smutty fan fiction etc. goes on the side blogs. As a side note, when you have a side blog you cannot like posts or ask questions as that side blog - it will be from your main blog.
10.) Try not to get disheartened if you create original content and it doesn’t get a lot of attention at first. When you create a blog it can take time to gain followers/traction. But remember as per point 1, that Tumblr should be fun and creating content should first and fore mostly be for you and your enjoyement. But if you continue to create, tag appropriately but also show appreciation for fellow creators there’s no reason why in time you won’t flourish. And as per point 3, if you reblog others work there’s a chance they in return will reblog your art.
11.) There’s extension kits you can get for tumblr, I know some people use them and find them helpful. I’m not sure they’re as poplar/needed now as they used to be. I used to use one but don’t feel the need now, however might be worth a google or asking someone more knowledgeable to see if it’ll work for you.
12.) You can blacklist tags through settings, if there’s any ships, characters, things you’d rather not see on your dash or that you find upsetting or triggering I’d recommend blacklisting them. If people tag correctly you shouldn’t much/if any of it.
13.) Under blog settings you can also choose whether you want your blog to be searchable via the email address you registered with and on google. I switched this off pretty much as soon as it became a feature! My blogs, even my main blog are a piece of me which is only shared with a select few people in real life. I really do not need my colleagues, employers, certain family/friends finding this!
14.) Use Queues! I adore a queue.... Once I discovered they were a thing I try to have around 100 posts in my queue on main at any time. You can amend how many times you post a day (mine is around 8-12 times, I change it when i go away). It just means your blog remains active even if you can’t really log on for a week or two or if you’re on holiday. Occasionally I’ll add original posts into my queue with writing, it can be nice to come back and see the feedback. A lot of people put ‘queue’ in the tag, but you’ll realise most people have a quirky tag. For example on main mine is - one does not simply queue their way through tumblr. And on my red dead blog it’s - I had a god damn queue! Sadly on here I haven’t got one yet!
15.) Finally I would say engage in discourse as little as possible. It can be tempting and while drama can be fun for a while, even just to watch from the outside it can quickly escalate into something nasty and toxic. At first you might want to join in but tumblr can be, well it can be a lot at times and very noisy with everyone screaming their opinions and trying to be louder than the person before. I would say no fandom is inherently toxic, but it happens. A fandom I was heavily involved in last year had so much discourse and there was so much drama that even though I wasn’t involved in it my anxiety was through the roof, I had a panic attack over it and felt paranoid. After speaking to other older members in the fandom I felt much better (they too were annoyed with what was happening) and we realised that essentially a lot of it boiled down to a real lack of critical thinking. I’m not saying don’t get involved at all, sometimes I have seen things where I’ve felt things need to be said/action taken especially when it comes to intolerance and hatred. But I would say when you do engage - pick your battles. (I hope this last one makes sense). I started writing a lot more and going into the politics of it and ranting about bigots and then thought that’s probably enough! 😁
I hope this post helps! Like I said I’ve never been asked something like this so it took a bit of thinking but these are some of the key thoughts I had.
edit - I meant to add that obviously the above is just my opinion and based on my experiences on tumblr/thoughts about things.
2 notes
·
View notes